Introduction to Bones and the Human Skeleton:
The bone is a rigid body tissue that makes up the individual bones of the human skeletal system and the skeletons of other vertebrates. The bone is a connective tissue that is made up of different types of cells. The two principal components of this material are- collagen and calcium phosphate; these two distinguish bone from other hard tissues such as chitin, enamel, and shell.
Difference between Skelatal and skeleton
Clarifying the Skeleton and the Skeletal System
Skeleton: It refers to the entire framework of bones in the human body, which provides structure and support to the body and protects internal organs. The Skeleton also helps the body to move and perform various physical activities.
Skeletal: It is a broad term related to skeleton. Its parts include bones, muscles, cartilage, and connective tissues. The term musculoskeletal system system refers to the bones and associated structures in the body that make up the skeleton
Functions of Bones:
Essential Functions of Bones in the Human Body
- Protection of Internal Organs:
- Bones protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
2. Mineral Reservoir:
- Bones act as a mineral reservoir for the storage of calcium and phosphate.
3. Structural Support:
- Bones provide structural support for the mechanical action of soft tissues.
4. Site for Blood Formation:
- Bones provide a protective site for specialized tissues such as the blood-forming system (bone marrow).
5. Storage of Fatty Acids:
- The adipose tissue in the bone marrow serves as a site for the storage of fatty acids.
Types of bones:
Exploring the Five Types of Bones in the Human Skeleton
Long Bones:
Long bones have a long, thin shape. Examples include the bones of the arms and legs (excluding the wrists, ankles, and kneecaps). With the help of muscles, long bones work as a lever to permit movement.
Short Bones:
Short bones have a squat, cubed shape. Examples include the bones that make up the wrists and the ankles.
Flat Bones:
Flat bones have a flattened, broad surface. Examples include ribs, shoulder blades, breast bones, and skull bones.
Sesamoid Bones:
Sesamoid bones are embedded in the tendons or muscles. Examples include the patella of the knee and the pisiform of the wrist.
Irregular Bones:
Irregular bones have a shape that does not conform to the above three types. Examples include the bones of the spine (vertebrae).
Structure of the Human Skeleton:
Detailed Overview of the Axial and Appendicular Skeletons
An adult human body consists of 206 bones in total. However, babies are born with 300 bones, which fuse to form the larger bones in the skeletal system. The human skeleton is divided into two main parts:
Axial Skeleton:
It comprises 80 bones, which include the skull, thoracic cage, and vertebral column.
Appendicular Skeleton:
It comprises 126 bones, which include the upper and lower limbs and the bones of the shoulder and pelvic girdles.
Complete list of 206 bones of the human body:
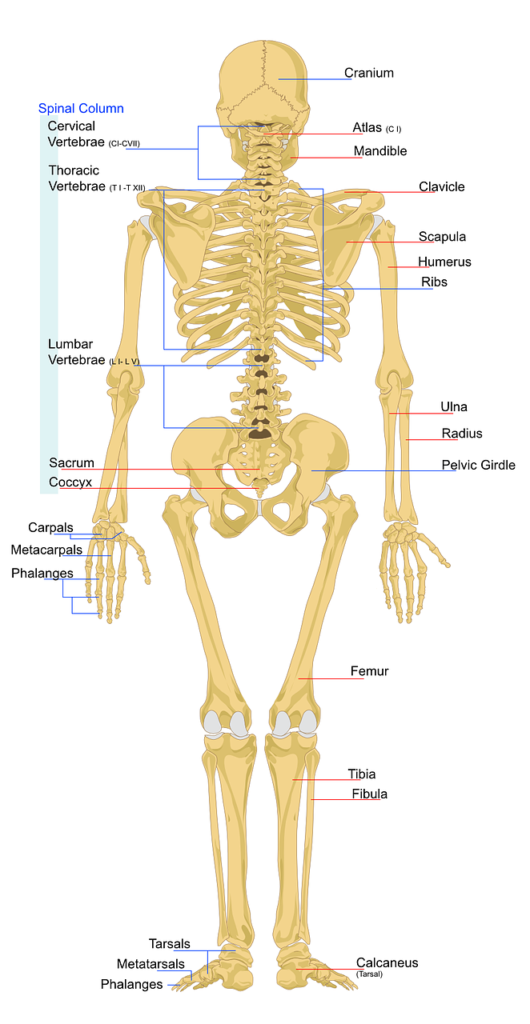
Comprehensive List of All 206 Bones in the Human Skeleton
Thoracic Region
Sterum (1 or3)
Ribs ( 24, in pairs)
Cervical ribs (present in some individuals)
Vertebrae
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum (5)
Coccyx (1)
Cranium
Occipital bone
Parietal bone (2)
Frontal bone
Temporal bones (2)
Ethmoid bone
Sphenoid bone
Facial bones
Lacrimal bones (2)
Maxillae (2)
Nasal bones (2)
Palatine bones (2)
Zygomatic bones (2)
Inferior nasal concha (2)
Mandible
Hyoid bone
Vomer
Auditory Ossicles
Malleus (2)
Incus (2)
Stapes (2)
Shoulder Girdle
Clavicle (2)
Scapula (2)
Upper Limbs
Humerus (2)
Radius (2)
Ulna (2)
Carpals (16)
Phanages (28)
Metacarpals (10)
Pelvic Region
Hip bones (2)
Lower Limbs
Femur (2)
Tibia (2)
Fibula (2)
Patella (2)
Tarsals (14)
Phalanges (28)
Metatarsals (10)
Conclusion:
The framework of the entire human body is made up of 206 bones, which include all different shapes and sizes of bones. These hard rigid connective tissue, which forms the bone, play one of the most important roles in human beings. They provides support and protection to all the essential and delicate organs of the human body, which are vital for the proper functioning.
Related Articles